Difference between revisions of "Set up Login System in Django"
(→Update settings.py) |
(→Initial Setup) |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | = | + | =Initial Setup= |
| + | Before you attempt this you should create a superuser in django, otherwise you won't have a username & password to test. | ||
| − | + | Run the DjangoAdmin program, choose the 'Manage' option and then 'createsuperuser'. | |
| + | |||
| + | ==Project URL's== | ||
| + | If you have created a django project by running the 'startproject' option of django-admin, it will create a folder which contains a file called 'urls.py'. This is the file used to define the URL's accepted by your web app. For a login/logout system we can use the built in django methods, and will mainly need to add code into this file. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Open the 'urls.py', you will need to import the following at the top of the page: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang=python> | <syntaxhighlight lang=python> | ||
| − | from django.contrib import | + | from django.contrib.auth import views as auth_views |
| − | + | </syntaxhighlight> | |
| − | + | ||
| + | Next, you will see a section which defines 'urlpatterns', we need to add some additional entries into this: | ||
| − | + | <syntaxhighlight lang=python> | |
| − | + | path('login/', auth_views.LoginView.as_view(), name='login'), | |
| − | + | path('logout/', auth_views.LogoutView.as_view(), name='logout'), | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | If you don't have a root path defined, look at the previous tutorial: [[Creating the Home page in Django]]. | |
| + | ==Settings== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now in the project folder you should see a file called 'settings.py', we need to add this line: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang=python> | <syntaxhighlight lang=python> | ||
| − | + | LOGIN_URL = 'login' | |
| − | + | LOGIN_REDIRECT_URL = '/' | |
| − | + | LOGOUT_REDIRECT_URL = '/' | |
| − | + | </syntaxhighlight> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | =User app= | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Create a new app in your project called 'users', then in this new folder edit the 'apps.py' file, you should see something like this: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | <syntaxhighlight lang=python> | |
| − | + | from django.apps import AppConfig | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | class UsersConfig(AppConfig): | |
| + | name = 'users' | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | Copy the name of the class, the example above is called UsersConfig. Now goto the 'settings.py' file and find the installed apps definition: | |
| − | + | <syntaxhighlight lang=python> | |
| + | INSTALLED_APPS = [ | ||
| + | 'django.contrib.admin', | ||
| + | 'django.contrib.auth', | ||
| + | 'django.contrib.contenttypes', | ||
| + | 'django.contrib.sessions', | ||
| + | 'django.contrib.messages', | ||
| + | 'django.contrib.staticfiles', | ||
| − | + | ] | |
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | Add a new entry at the start of this list for your app: | |
| − | <syntaxhighlight lang= | + | <syntaxhighlight lang=python> |
| − | + | INSTALLED_APPS = [ | |
| − | + | 'users.apps.UsersConfig', | |
| − | + | 'django.contrib.admin', | |
| − | + | 'django.contrib.auth', | |
| − | + | 'django.contrib.contenttypes', | |
| − | + | 'django.contrib.sessions', | |
| − | + | 'django.contrib.messages', | |
| − | + | 'django.contrib.staticfiles', | |
| − | + | ] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | =User Templates= | |
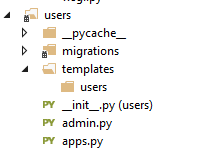
| + | In the folder for your users app, create a folder called templates. Inside this create a folder called users: | ||
| − | + | [[File:Template folder.png]] | |
| − | |||
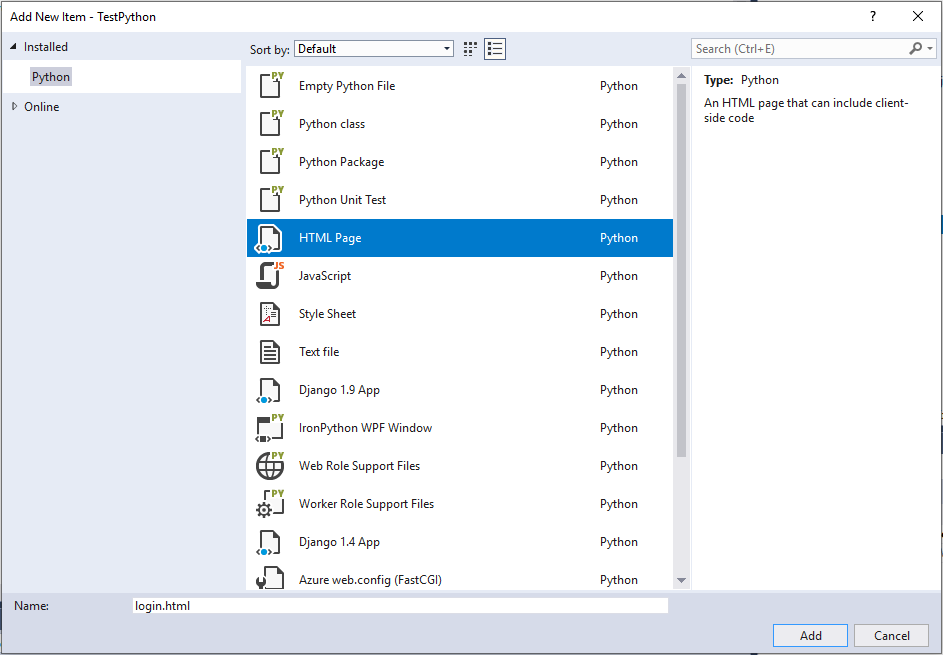
| − | + | Now in this folder add a new item, and select 'HTML' and call it 'login.html': | |
| − | + | [[File:New html.png]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Now replace the whole html code with this (the previous tutorial created 'base.html'): | |
<syntaxhighlight lang=html> | <syntaxhighlight lang=html> | ||
| − | {% extends | + | {% extends "MyApp/base.html" %} |
| − | |||
| − | |||
{% block content %} | {% block content %} | ||
| Line 94: | Line 92: | ||
</form> | </form> | ||
{% endblock %} | {% endblock %} | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now back in 'urls.py', find: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang=python> | ||
| + | path('login/', auth_views.LoginView.as_view(), name='login'), | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now inside the round brackets after '.as_view' enter: | ||
| + | |||
| + | template_name='users/login.html' | ||
| + | |||
| + | So it should be: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang=python> | ||
| + | path('login/', auth_views.LoginView.as_view(template_name='users/login.html' ), name='login'), | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Edit the Base.HTML= | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the 'base.html' file find the following section: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang=html> | ||
| + | <ul class="nav navbar-nav navbar-right"> | ||
| + | <li><a href="#"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-user"></span> Sign Up</a></li> | ||
| + | <li><a href="#"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-log-in"></span> Login</a></li> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Change this section to this: | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang=html> | ||
| + | <ul class="nav navbar-nav navbar-right"> | ||
| + | {% if user.is_authenticated %} | ||
| + | <li><a href="{% url 'logout' %}"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-log-out"></span> LogOut</a></li> | ||
| + | {% else %} | ||
| + | <li><a href="#"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-user"></span> Sign Up</a></li> | ||
| + | <li><a href="{% url 'login' %}"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-log-in"></span> Login</a></li> | ||
| + | {% endif %} | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Latest revision as of 08:41, 11 September 2019
Contents
Initial Setup
Before you attempt this you should create a superuser in django, otherwise you won't have a username & password to test.
Run the DjangoAdmin program, choose the 'Manage' option and then 'createsuperuser'.
Project URL's
If you have created a django project by running the 'startproject' option of django-admin, it will create a folder which contains a file called 'urls.py'. This is the file used to define the URL's accepted by your web app. For a login/logout system we can use the built in django methods, and will mainly need to add code into this file.
Open the 'urls.py', you will need to import the following at the top of the page:
from django.contrib.auth import views as auth_views
Next, you will see a section which defines 'urlpatterns', we need to add some additional entries into this:
path('login/', auth_views.LoginView.as_view(), name='login'),
path('logout/', auth_views.LogoutView.as_view(), name='logout'),
If you don't have a root path defined, look at the previous tutorial: Creating the Home page in Django.
Settings
Now in the project folder you should see a file called 'settings.py', we need to add this line:
LOGIN_URL = 'login'
LOGIN_REDIRECT_URL = '/'
LOGOUT_REDIRECT_URL = '/'
User app
Create a new app in your project called 'users', then in this new folder edit the 'apps.py' file, you should see something like this:
from django.apps import AppConfig
class UsersConfig(AppConfig):
name = 'users'
Copy the name of the class, the example above is called UsersConfig. Now goto the 'settings.py' file and find the installed apps definition:
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
]
Add a new entry at the start of this list for your app:
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'users.apps.UsersConfig',
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
]
User Templates
In the folder for your users app, create a folder called templates. Inside this create a folder called users:
Now in this folder add a new item, and select 'HTML' and call it 'login.html':
Now replace the whole html code with this (the previous tutorial created 'base.html'):
{% extends "MyApp/base.html" %}
{% block content %}
<h2>Login</h2>
<form method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form.as_p }}
<button type="submit">Login</button>
</form>
{% endblock %}
Now back in 'urls.py', find:
path('login/', auth_views.LoginView.as_view(), name='login'),
Now inside the round brackets after '.as_view' enter:
template_name='users/login.html'
So it should be:
path('login/', auth_views.LoginView.as_view(template_name='users/login.html' ), name='login'),
Edit the Base.HTML
In the 'base.html' file find the following section:
<ul class="nav navbar-nav navbar-right">
<li><a href="#"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-user"></span> Sign Up</a></li>
<li><a href="#"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-log-in"></span> Login</a></li>
</ul>
Change this section to this:
<ul class="nav navbar-nav navbar-right">
{% if user.is_authenticated %}
<li><a href="{% url 'logout' %}"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-log-out"></span> LogOut</a></li>
{% else %}
<li><a href="#"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-user"></span> Sign Up</a></li>
<li><a href="{% url 'login' %}"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-log-in"></span> Login</a></li>
{% endif %}
</ul>