Difference between revisions of "Number Systems / Number Bases"
(→Denary Number system) |
(→TRC PowerPoint) |
||
| (54 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | =Overview= | ||
| + | ===CraigNDave=== | ||
| + | <youtube>HIRB99gDmB8</youtube> | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HIRB99gDmB8&list=PLCiOXwirraUCa2MYf_oSM94uvwIGPMZ1q | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Computer Science Tutor=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <youtube>Ol3PxSpEeT4</youtube> | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ol3PxSpEeT4&list=PL04uZ7242_M6O_6ITD6ncf7EonVHyBeCm | ||
| + | |||
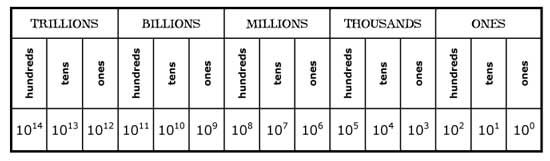
=Number Systems= | =Number Systems= | ||
| − | The number systems used in Computer Science are often referred to as Base 16, Base 10, Base 8, or Base 2. | + | The number systems used in Computer Science are often referred to as Base 16, Base 10, Base 8, or Base 2. |
| + | |||
The number base specifies how many digits are used (Including Zero) and how much each digit is multiplied by as it is moved from right to left. | The number base specifies how many digits are used (Including Zero) and how much each digit is multiplied by as it is moved from right to left. | ||
| − | =Denary Number | + | |
| + | [[File:Bases.jpg|300px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Denary Number System= | ||
Also sometimes referred to as the Decimal number system, the Denary number system uses the digits 0-9 which means there are 10 possible digits. | Also sometimes referred to as the Decimal number system, the Denary number system uses the digits 0-9 which means there are 10 possible digits. | ||
| + | |||
If we go beyond the digit 9 in denary another column is used; i.e the ‘tens’ column or the ‘Hundreds’ Column. | If we go beyond the digit 9 in denary another column is used; i.e the ‘tens’ column or the ‘Hundreds’ Column. | ||
| + | |||
This means the number 10 in denary would be 1 ‘ten’ plus 0 ‘units’ | This means the number 10 in denary would be 1 ‘ten’ plus 0 ‘units’ | ||
| + | |||
The first column, the one on the far right, s 10 to the power 0. For each subsequent column the power is increased by 1. | The first column, the one on the far right, s 10 to the power 0. For each subsequent column the power is increased by 1. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 30: | ||
=Binary Number System= | =Binary Number System= | ||
| + | The Binary number system is an essential system as all digital content is stored using binary, Binary is the base 2 number system. | ||
| + | Unlike other systems binary uses only two different digits 0 and 1 to represent any given number. | ||
| + | 0 is represented as 0, and 1 is represented as 1 and just like the decimal system if the value exceeds 1 an additional column is needed. | ||
| + | As binary is in base 2 it uses twos instead of tens which the decimal system uses. | ||
| + | So for example 10 would translate to 8 plus 0 plus 2 plus 0 and would read 1010. The Zeros are present to show the columns 2² and 2° | ||
| + | The first column on the far right is 2 to the power 0, for each subsequent column the power is increased by 1. | ||
| + | <table style="width:100%; border-style: solid;border-width: thin;" class="wikitable"> | ||
| + | <tr style=""> | ||
| + | <th style="width:11%;text-align:left !important;">Value</th> | ||
| + | <th style="width:11%;text-align:left !important;">128's</th> | ||
| + | <th style="width:11%;text-align:left !important;">64's</th> | ||
| + | <th style="width:11%;text-align:left !important;">32's</th> | ||
| + | <th style="width:11%;text-align:left !important;">16's</th> | ||
| + | <th style="width:11%;text-align:left !important;">8's</th> | ||
| + | <th style="width:11%;text-align:left !important;">4's</th> | ||
| + | <th style="width:11%;text-align:left !important;">2's</th> | ||
| + | <th style="width:11%;text-align:left !important;">1's</th> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td style="width:11%;">Power<br></td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:11%;">2<sup>7</sup></td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:11%;">2<sup>6</sup></td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:11%;">2<sup>5</sup></td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:11%;">2<sup>4</sup></td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:11%;">2<sup>3</sup></td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:11%;">2<sup>2</sup></td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:11%;">2<sup>1</sup></td> | ||
| + | <td style="width:11%;">2<sup>0</sup></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Binary== | ||
| + | <youtube>https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y0QL02-bnhs&list=PLCiOXwirraUDGCeSoEPSN-e2o9exXdOka&index=0</youtube> | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y0QL02-bnhs&list=PLCiOXwirraUDGCeSoEPSN-e2o9exXdOka&index=0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Binary Range== | ||
| + | <youtube>https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5-jez-dvY7Y&list=PLCiOXwirraUDGCeSoEPSN-e2o9exXdOka&index=1</youtube> | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5-jez-dvY7Y&list=PLCiOXwirraUDGCeSoEPSN-e2o9exXdOka&index=1 | ||
| + | |||
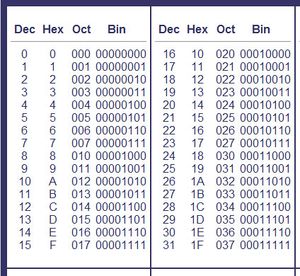
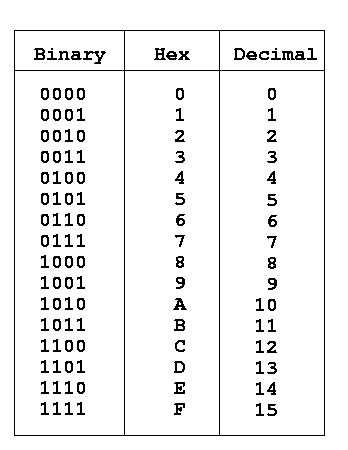
| + | =Hexadecimal Number System= | ||
| + | Hexadecimal is base 16 meaning it has 16 different digits, 0 to 15. | ||
| + | The numbers 0 to 9 are the same as denary, but the numbers 10 to 15 use the letters A to F. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:dec_hex_bin.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The first column on the far right is 16 to the power 0 for each subsequent column the power is increased by 1. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Hexidecimal Powers.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Revision Questions= | ||
| + | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | What is the base 16 number system called? | ||
| + | { Hexadecimal|hexadecimal } | ||
| + | ||The name of the base 16 number system is Hexadecimal. | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | What is the base 10 number system called? | ||
| + | { Decimal|decimal|Denary|denary } | ||
| + | ||The name of the base 10 number system is Decimal or Denary | ||
| + | ||Denary is base 10 because it had ten numbers that it uses, i.e. 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | What base system is Binary? | ||
| + | |type="()"} | ||
| + | - Base 16 | ||
| + | || Base 16 is Hexadecimal | ||
| + | - Base 10 | ||
| + | || Base 10 is Denary | ||
| + | + Base 2 | ||
| + | || Base 2 is Binary | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | In Hexadecimal the numbers 10-15 are represented by the letters A-F | ||
| + | |type="()"} | ||
| + | + True | ||
| + | -False | ||
| + | || Hex goes from 1-9 then goes from A to F; A = 10, B = 11, C = 12 etc... | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | All digital content is stored using Binary | ||
| + | |type="()"} | ||
| + | + True | ||
| + | -False | ||
| + | || Computers can only understand Binary information. | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | What is the Hexadecimal number B5 in Binary? | ||
| + | { 10110101 } | ||
| + | ||B = 11 | ||
| + | ||11 in Binary is 1011 | ||
| + | || 5 in Binary is 0101 | ||
| + | ||10110101 | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | |type="{}" } | ||
| + | What is the Denary number 7 in Binary? | ||
| + | { 0111 } | ||
| + | || 0111 means we have a 1, a 2 and a 4... | ||
| + | || 1 + 2 + 4 = 7 | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | 10 in Binary is represented as 1001 | ||
| + | |type="()"} | ||
| + | -True | ||
| + | +False | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | The Hexadecimal number 34 is 00110100 | ||
| + | |type="()"} | ||
| + | +True | ||
| + | -False | ||
| + | |||
| + | { | ||
| + | |type="{}"} | ||
| + | What is 16 to the power of 0? | ||
| + | { 1 } | ||
| + | || Anything to the power of 0 is 1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | </quiz> | ||
Latest revision as of 09:23, 25 September 2020
Contents
[hide]Overview
CraigNDave
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HIRB99gDmB8&list=PLCiOXwirraUCa2MYf_oSM94uvwIGPMZ1q
Computer Science Tutor
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ol3PxSpEeT4&list=PL04uZ7242_M6O_6ITD6ncf7EonVHyBeCm
Number Systems
The number systems used in Computer Science are often referred to as Base 16, Base 10, Base 8, or Base 2.
The number base specifies how many digits are used (Including Zero) and how much each digit is multiplied by as it is moved from right to left.
Denary Number System
Also sometimes referred to as the Decimal number system, the Denary number system uses the digits 0-9 which means there are 10 possible digits.
If we go beyond the digit 9 in denary another column is used; i.e the ‘tens’ column or the ‘Hundreds’ Column.
This means the number 10 in denary would be 1 ‘ten’ plus 0 ‘units’
The first column, the one on the far right, s 10 to the power 0. For each subsequent column the power is increased by 1.
Binary Number System
The Binary number system is an essential system as all digital content is stored using binary, Binary is the base 2 number system. Unlike other systems binary uses only two different digits 0 and 1 to represent any given number. 0 is represented as 0, and 1 is represented as 1 and just like the decimal system if the value exceeds 1 an additional column is needed. As binary is in base 2 it uses twos instead of tens which the decimal system uses. So for example 10 would translate to 8 plus 0 plus 2 plus 0 and would read 1010. The Zeros are present to show the columns 2² and 2° The first column on the far right is 2 to the power 0, for each subsequent column the power is increased by 1.
| Value | 128's | 64's | 32's | 16's | 8's | 4's | 2's | 1's |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power |
27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 |
Binary
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y0QL02-bnhs&list=PLCiOXwirraUDGCeSoEPSN-e2o9exXdOka&index=0
Binary Range
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5-jez-dvY7Y&list=PLCiOXwirraUDGCeSoEPSN-e2o9exXdOka&index=1
Hexadecimal Number System
Hexadecimal is base 16 meaning it has 16 different digits, 0 to 15. The numbers 0 to 9 are the same as denary, but the numbers 10 to 15 use the letters A to F.
The first column on the far right is 16 to the power 0 for each subsequent column the power is increased by 1.