Difference between revisions of "Select Queries"
(→Basic Quiz) |
|||
| (25 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==The Basic Construct== | ==The Basic Construct== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang=sql> | <syntaxhighlight lang=sql> | ||
| − | SELECT | + | SELECT [data] FROM [table] |
| − | WHERE | + | WHERE [condition] |
| − | ORDER BY | + | ORDER BY [data] (DESC) ; |
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <strong>ORDER BY</strong> is set to ''Ascending'' by default. Adding DESC for ''Descending'' will turn this list upside-down. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Basic Example== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang=sql> | ||
| + | SELECT * FROM Book | ||
| + | WHERE Price > 100.00 | ||
| + | ORDER BY Title; | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Remember the '''SELECT''' can have * to select all fields, however questions will normally specify what fields to select. The '''FROM''' section should identify which table(s) to select the data from. The '''WHERE''' section should include the criteria used to select the data, this could be a simple statement as above but remember you can also include other operators such as '''AND''', '''OR''', '''NOT''', '''LIKE''', and so on. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Relational Databases & Select== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Using a relational database (two or more related tables) makes the select statement more complex because you can obviously select data from multiple tables and also use criteria on multiple tables in the where section. So: | ||
| + | #Any field name which causes ambiguity must also have the table specified, ie table.fieldname | ||
| + | #The from section must include the tables for every field in the where or select sections | ||
| + | #The where section must contain the criteria to explain how the tables in the from section are related | ||
| + | |||
| + | So for example: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :*this should be primary key to foreign key, so if you have just 2 tables - table1.primary = table2.foreign | ||
| + | :* 3 tables would have something like table1.primary = table2.foreign AND table1.primary = table3.foreign | ||
| + | |||
| + | Remember this is on top of the criteria you need to use for the question or output required. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Relational Databases & Select Example== | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang=sql> | ||
| + | SELECT TutorGroup.Name, Student.Name | ||
| + | FROM TutorGroup, Student | ||
| + | WHERE Student.ID = TutorGroup.StudentID | ||
| + | AND Student.YearGroup = 12 AND Student.Gender = 'Male' | ||
| + | ORDER BY TutorGroup.Name; | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This would create a list of male students in year group 12 in order of TutorGroup.Name, for each record it will select TutorGroup.Name and Student.Name. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Basic Quiz=== | ||
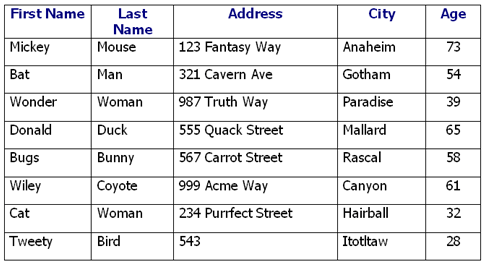
| + | All these questions will use this table called Employees: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Capture.png]] | ||
| + | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {which of the following Select queries will select the 'First Name' and 'Last Name' of every record? | ||
| + | |type="()"} | ||
| + | + Select 'First Name', 'Last Name' from Employees | ||
| + | ||Correct | ||
| + | - Select * from Employees | ||
| + | ||Incorrect | ||
| + | - Select All from Employees | ||
| + | ||Incorrect | ||
| + | - Select 'First Name' from Employees | ||
| + | ||Incorrect | ||
| + | |||
| + | {which of the following Select queries will select the 'First Name' and 'Last Name' of every employee with the 'Last Name' of 'woman'? | ||
| + | |type="()"} | ||
| + | - Select 'First Name', 'Last Name' from Employees where Employee 'Last Name' = 'woman' | ||
| + | ||Incorrect | ||
| + | + Select 'First Name', 'Last Name' from Employees where 'Last Name' = 'woman' | ||
| + | ||Correct | ||
| + | - Select * from Employees where 'Last Name' = 'woman' | ||
| + | ||Incorrect | ||
| + | - Select * from Employees where Employee 'Last Name' = 'woman' | ||
| + | ||Incorrect | ||
| + | |||
| + | {which of the following Select queries will select the 'First Name' and 'Last Name' of every employee over the age of 50? | ||
| + | |type="()"} | ||
| + | - Select 'First Name', 'Last Name' from Employees where Employee 'Age' < 50 | ||
| + | ||Incorrect | ||
| + | - Select 'First Name', 'Last Name' from Employees where 'Age' < 50 | ||
| + | ||Incorrect | ||
| + | - Select 'First Name', 'Last Name' from Employees where Employee 'Age' > 50 | ||
| + | ||Incorrect | ||
| + | + Select 'First Name', 'Last Name' from Employees where 'Age' > 50 | ||
| + | ||Correct | ||
| + | |||
| + | {which of the following Select queries will select the 'First Name' and 'Last Name' of every employee over the age of 50 but under the age of 75? | ||
| + | |type="()"} | ||
| + | - Select 'First Name', 'Last Name' from Employees where Employee 'Age' < 50 And 'Age' > 75 | ||
| + | ||Incorrect | ||
| + | - Select 'First Name', 'Last Name' from Employees where 'Age' < 50 And < 75 | ||
| + | ||Incorrect | ||
| + | - Select 'First Name', 'Last Name' from Employees where 'Age' > 50 And <75 | ||
| + | ||Incorrect | ||
| + | + Select 'First Name', 'Last Name' from Employees where 'Age' > 50 And Age <75 | ||
| + | ||Correct | ||
| + | |||
| + | {which of the following Select queries will select the 'First Name' and 'Last Name' of every record in alphabetical order by 'Last Name'? | ||
| + | |type="()"} | ||
| + | + Select 'First Name', 'Last Name' from Employees Order By 'Last Name' | ||
| + | ||Correct | ||
| + | - Select 'First Name', 'Last Name' from Employees Order By 'Last Name' Desc | ||
| + | ||Incorrect | ||
| + | - Select 'First Name', 'Last Name' from Employees OrderBy 'Last Name' | ||
| + | ||Incorrect | ||
| + | - Select 'First Name', 'Last Name' from Employees OrderBy 'Last Name' Desc | ||
| + | ||Incorrect | ||
| + | </quiz> | ||
Latest revision as of 09:59, 28 September 2020
- Used for fetching information from an SQL database.
- 'Outputs' the data once successfully selected
- Allows selection from multiple tables but not multiple databases.
Contents
The Basic Construct
SELECT [data] FROM [table]
WHERE [condition]
ORDER BY [data] (DESC) ;
ORDER BY is set to Ascending by default. Adding DESC for Descending will turn this list upside-down.
Basic Example
SELECT * FROM Book
WHERE Price > 100.00
ORDER BY Title;
Remember the SELECT can have * to select all fields, however questions will normally specify what fields to select. The FROM section should identify which table(s) to select the data from. The WHERE section should include the criteria used to select the data, this could be a simple statement as above but remember you can also include other operators such as AND, OR, NOT, LIKE, and so on.
Relational Databases & Select
Using a relational database (two or more related tables) makes the select statement more complex because you can obviously select data from multiple tables and also use criteria on multiple tables in the where section. So:
- Any field name which causes ambiguity must also have the table specified, ie table.fieldname
- The from section must include the tables for every field in the where or select sections
- The where section must contain the criteria to explain how the tables in the from section are related
So for example:
- this should be primary key to foreign key, so if you have just 2 tables - table1.primary = table2.foreign
- 3 tables would have something like table1.primary = table2.foreign AND table1.primary = table3.foreign
Remember this is on top of the criteria you need to use for the question or output required.
Relational Databases & Select Example
SELECT TutorGroup.Name, Student.Name
FROM TutorGroup, Student
WHERE Student.ID = TutorGroup.StudentID
AND Student.YearGroup = 12 AND Student.Gender = 'Male'
ORDER BY TutorGroup.Name;
This would create a list of male students in year group 12 in order of TutorGroup.Name, for each record it will select TutorGroup.Name and Student.Name.
Basic Quiz
All these questions will use this table called Employees: