Difference between revisions of "Compression"
(→TRC PowerPoint) |
|||
| (65 intermediate revisions by 15 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | = | + | =Overview= |
Data compression is decreasing the size of a file. There are many different compression techniques. | Data compression is decreasing the size of a file. There are many different compression techniques. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Computer Science Tutor=== | ||
| + | <youtube>v1u-vY6NEmM</youtube> | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v1u-vY6NEmM&list=PL04uZ7242_M6O_6ITD6ncf7EonVHyBeCm&index=10 | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Uses of compression= | ||
| + | Compression is used to reduce the storage space that is required to store a file. But since disk space is becoming less and less of a problem, compression's new main use is sending stuff through the internet. The reduced file size helps to reduce the amount of buffering that is required whilst retaining the quality. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Lossy vs Lossless= | ||
| + | |||
| + | <youtube> https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DuzD-LSanzM&list=PLCiOXwirraUA69WUAMYyFicC5qbQ4PGc4 </youtube> | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DuzD-LSanzM&list=PLCiOXwirraUA69WUAMYyFicC5qbQ4PGc4 | ||
==Lossy Compression== | ==Lossy Compression== | ||
| − | Lossy compression is a compression technique that decreases file size by discarding bits of unnecessary data. This means that the original file cannot be recreated. | + | Lossy compression is a compression technique that decreases file size by discarding bits of unnecessary data. This means that the original file cannot be recreated. Lossy compression will create a new image which is similar to the original, but has a reduced quality. Another example of lossy compression is used to reduce the file size of a sound file by reducing the bitrate used in the original. |
| − | + | ||
| + | All of the above use lossy methods of compression to save data and space. This isn't the best method to use as it gets rid of some of the data, so this would be a unsuitable method to use if the original file needs to be used. Lossy compression cannot be used on binary or text files because all data is needed to convey the correct meaning. People who would need the original file would be: Photographers, Audio Producers and Printing Firms. These could produce lossy compressed images for sample purposes or as draft prints. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lossy compression is also ideal for online pages, as it allows faster load times due to a lower amount of data being loaded. | ||
===Lossy Methods=== | ===Lossy Methods=== | ||
| + | Some methods used are to delete sounds which are not heard, either because of the frequency or if another sound will drown it out. Images could be compressed more in the background than the foreground, the focus is the foreground so compression will not be noticed in the background. Also images could merge together adjacent colours just like the human eye. A pixel of black next to a pixel of white will actually be seen as two grey pixels. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lossy compression formats: | ||
| + | * JPEG (image) | ||
| + | * MPEG-1 (video) | ||
| + | * MP3 (audio) | ||
| + | ====JPEG==== | ||
| + | JPEG stands for "Joint Photographic Experts Group". | ||
| + | The JPEG format uses an algorithm in order to remove details that will not be seen by the human eye. It also reduces the quality of the background of the image since the main focus will be on the foreground or the main focus of the image. This helps reduce the file size whilst not reducing the main focus of the image. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====MP3==== | ||
| + | MP3 stands for MPEG-2 audio layer 3. It uses different techniques such as removing inaudible frequencies and removing sounds that will be drowned out by louder noises. Bitrate is the number of bits a second that are encoded by MP3 per second. A higher bitrate will lead to a better quality sound at the cost of a larger file whilst a low bitrate will reduce the file size at the expense of sound quality. A variable bitrate is available in which the bitrate adapts to the sound in different parts of the recording. | ||
==Lossless Compression== | ==Lossless Compression== | ||
| − | Lossless compression is a compression technique that decreases file size | + | Lossless compression is a compression technique that decreases file size while keeping all of the data. This means there is no loss in quality, and the original file can be recreated exactly as it was prior to compression. |
| − | Examples of lossless compression | + | |
| + | This is possible because of repeating patterns in the data. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Examples of lossless compression methods include Run Length Encoding and Dictionary Based Methods. Run Length Encoding replaces repeating pixels or codes. Dictionary Based Methods rely on patterns within a file and are more effective with larger files. Each pattern can has an ID number. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Lossless compression formats: | ||
| + | *FLAC (Audio) | ||
| + | *WAV (Audio) | ||
| + | *PNG (Image) | ||
| + | *BMP (Image) | ||
| + | (Note that there are not many types of lossless video compression, the closest being H.264, as the file size tends to be smaller to start with) | ||
| + | |||
| + | <youtube>https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M3zJT8gmfxE&list=PLCiOXwirraUA69WUAMYyFicC5qbQ4PGc4</youtube> | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M3zJT8gmfxE&list=PLCiOXwirraUA69WUAMYyFicC5qbQ4PGc4 | ||
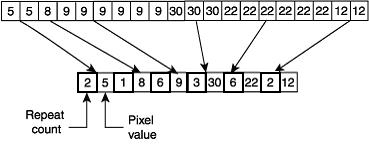
===Run Length Encoding=== | ===Run Length Encoding=== | ||
| + | This method of lossless compression counts the bits that are repeated consecutively. For example, if a picture contained 3 red pixels one after the other, rather than storing each pixel individually, the file would instead store the pixel colour and the amount of times it is repeated. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Run Len Enc.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | However, if a file does not contain many repetitions then this method of compression can actually increase file size, as a single pixel would be stored as its colour and then the information that it is repeated only once. | ||
===Dictionary Based Methods=== | ===Dictionary Based Methods=== | ||
| + | This is used when there are lots of repeating patterns of data. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For example, when writing a document about Computer Science, key words like "Computer Science" would be repeated throughout the document. Instead of storing the bit pattern for the word over and over, it stores the phrase in a dictionary with a reference number and stores the number in place of the phrase. This means that whenever the phrase is needed, it calls up the dictionary and replaces that number with the phrase. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A disadvantage of this method is that additional data is needed to store the dictionary as well as the file. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Difference between lossy and lossless compression== | ||
| + | The main difference between lossy and lossless compression is the fact that when compressed, lossy loses some of the original quality*, whilst lossless retains all of the initial quality, hence the names "lossy" and "lossless". | ||
| + | |||
| + | Although sometimes lossy compression only removes the information that is not needed, for example it may remove some of the frequencies that cannot be heard by humans, so in this sense the reduced quality may not be detected. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The only other main difference is that, due to compression methods, lossy tends to be of a lesser file size when compressed, as some duplicate or unnecessary information tends to be left out, although this can also depend, as the original file might not have any duplicate or unnecessary information, in which case, the file size would be the same. | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Revision Questions= | ||
| + | '''try to add more questions on: | ||
| + | *lossless compression | ||
| + | *run length encoding | ||
| + | *dictionary based methods | ||
| + | *lossy vs lossless | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Also '||' is the feedback for an answer, and could be greatly improved''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {Which of the following is the correct definition for lossy compression? | ||
| + | | type="()" } | ||
| + | - Lossy file compression does not discard parts of a file, but it does reduce file size by merging colours and pixels. | ||
| + | || This is more accurate for lossless compression. | ||
| + | - Lossy file compression simply stores instructions on how to reproduce the image. So instead of storing pixels and colours, instructions are actually stored, which reduces file size. | ||
| + | || Lossy compression does not convert the image to instructions. | ||
| + | + Lossy file compression discards parts of a file that aren't that important to save space, it also merges colours and pixels which lowers colour depth in order to save more space. All in all, resolution is reduced and space is saved. | ||
| + | || Correct | ||
| + | - Lossy file compression saves space by reducing the size/dimensions of an image. | ||
| + | || Lossy compression can remove parts of an image but it won't really change the dimensions of an image, it reduces the resolution. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {Which of the following is the correct definition for lossless compression? | ||
| + | | type="()" } | ||
| + | - Lossless file compression discards unimportant information from the file, and merges colours and pixels to save space. | ||
| + | || Lossless compression does not discard information from the file. | ||
| + | + Lossless file compression retains all information allowing the file to be uncompressed to its original state. | ||
| + | || Correct. Lossless file compression does not lose any information about the file. | ||
| + | - Lossless file compression simply stores instructions on how to reproduce the image. So instead of storing pixels and colour, instructions are actually stored, which reduces file size. | ||
| + | || Lossless file compression does not store the file as instructions. | ||
| + | - Lossless file compression saves space by reducing the size/dimensions of an image. | ||
| + | || Lossless compression does not involve reducing the quality of the image. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {Which of the following formats can lossy compression be used on | ||
| + | | type="[]" } | ||
| + | -ZIP | ||
| + | || ZIP Uses lossless compression | ||
| + | +JPEG | ||
| + | || Correct | ||
| + | -PNG | ||
| + | || PNG Uses lossless compression | ||
| + | +MPEG-1 | ||
| + | || Correct | ||
| + | +MP3 | ||
| + | || Correct | ||
| + | -TXT | ||
| + | || TXT Uses lossless compression | ||
| + | |||
| + | {Which file formats below can lossless compression be used on? | ||
| + | | type="[]" } | ||
| + | + PNG | ||
| + | || Correct | ||
| + | + ZIP | ||
| + | || Correct | ||
| + | - JPEG | ||
| + | || JPEG uses lossy compression | ||
| + | + TXT | ||
| + | || Correct | ||
| + | - MPEG-1 | ||
| + | || MPEG-1 uses lossy compression | ||
| + | - MP3 | ||
| + | || MP3 uses lossy compression | ||
| + | |||
| + | {What are the two common methods of compression ? | ||
| + | | type="[]"} | ||
| + | + Lossy | ||
| + | || Correct | ||
| + | - Loss | ||
| + | || Incorrect, loss compression is not real. | ||
| + | - Lossful | ||
| + | || Incorrect, lossful compression is not real. | ||
| + | + Lossless | ||
| + | || Correct | ||
| + | |||
| + | {What file format would be the best to use for a logo? | ||
| + | | type="()"} | ||
| + | - MP3 | ||
| + | || Not an image format | ||
| + | + JPEG | ||
| + | || Correct, as a logo would likely be small on a webpage the extra detail which is lost in this format wouldn't be noticeable | ||
| + | - PNG | ||
| + | || A JPEG would likely be better | ||
| + | - ZIP | ||
| + | || Not an image format | ||
| + | |||
| + | {What file format would be the best to use for a song on your phone? | ||
| + | | type="()"} | ||
| + | - JPEG | ||
| + | || Not a sound format | ||
| + | - WAV | ||
| + | || MP3 would be better | ||
| + | - TXT | ||
| + | || Not a sound format | ||
| + | + MP3 | ||
| + | || The best choice as the lost data would likely not be noticed | ||
| + | |||
| + | {What definition fits Run Length Encoding best? | ||
| + | | type"()"} | ||
| + | - A form of lossy data compression which records a value and how many times it is repeated | ||
| + | || Incorrect, RLE is used in lossless data compression. | ||
| + | + A form of lossless data compression which records a value and how many times it is repeated | ||
| + | || Correct | ||
| + | - A form of lossy data compression which reduces the resolution and dimensions of an image | ||
| + | || Incorrect, RLE does not reduce the quality of an image. | ||
| + | - A form of lossless data compression which reduces the resolution and dimensions of an image | ||
| + | || Incorrect, RLE does not reduce the quality of an image. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {Which of the following are types of lossless compression? | ||
| + | | type="[]"} | ||
| + | - Huffpuff trees | ||
| + | || Not a type of any form of compression. | ||
| + | + Huffman trees | ||
| + | || Huffman trees are a type of dictionary method compression, it is thus lossless. | ||
| + | - Run time encoding | ||
| + | || This is close to a correct method of compression. | ||
| + | + Run length encoding | ||
| + | || Run length encoding compresses by recording a value and then how many times it is repeated. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {When is a dictionary based method used? | ||
| + | | type="()"} | ||
| + | - It is used when there aren't many repeating patterns | ||
| + | || This is incorrect as compressing this way could possibly increase file size. | ||
| + | + It is used when there are repeating patterns of data | ||
| + | || This is correct. | ||
| + | - It is used to compress only text, books etc. | ||
| + | || Incorrect, it can be used to compress images. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {Calculate the file size in bytes when an image with 8 bit colour at a resolution of 4x4 is compressed with run length encoding. (Assume there are only 3 colours)[[File:4x4RunLengthEncoding.png]] | ||
| + | | type"()"} | ||
| + | - 19 Bytes | ||
| + | || Incorrect, there are 3 colours, encoded it looks like g2y7b7. You don't treat the 2, 7 and 7 as integers when you add them, you add the amount of characters there are. | ||
| + | + 6 Bytes | ||
| + | || Correct, there are 3 colours, encoded it looks like g2y7b7. 1 byte for the colour and 1 byte for the repeated number. | ||
| + | - 42 Bits | ||
| + | || The question asked for the answer to be in bytes, this is the correct answer but in the wrong format. | ||
| + | - 6 Bits | ||
| + | || The question asked for the answer to be in bytes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {Name a dictionary based method. | ||
| + | | type="()"} | ||
| + | - Run length encoding | ||
| + | || Run length encoding is a specific type of lossless compression and does not fall under the dictionary based methods | ||
| + | + Huffman trees | ||
| + | || Correct, Huffman trees are dictionary based methods, they use frequency of characters to determine the bit depth of the character. More frequent characters get a shorter binary | ||
| + | |||
| + | {Which of the following apply to lossy compression. | ||
| + | | type="[]"} | ||
| + | -They provide a higher quality than lossless methods | ||
| + | || Lossless retains all information whereas lossy compression loses data permanently | ||
| + | + Lossy compression will never result in a greater file size, whereas lossless compression may result in a larger size. | ||
| + | || This is correct, lossless compression can sometimes result in a greater file size. | ||
| + | + Lossy compression can be accessed while compressed whereas oftentimes, lossless compression must first be uncompressed. | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | - Lossless compression is always a better choice | ||
| + | || Lossy compression is sometimes more suitable, for example when you have a logo on a website, lossy compression will be less noticable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | </quiz> | ||
Latest revision as of 09:27, 25 September 2020
Overview
Data compression is decreasing the size of a file. There are many different compression techniques.
Computer Science Tutor
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v1u-vY6NEmM&list=PL04uZ7242_M6O_6ITD6ncf7EonVHyBeCm&index=10
Uses of compression
Compression is used to reduce the storage space that is required to store a file. But since disk space is becoming less and less of a problem, compression's new main use is sending stuff through the internet. The reduced file size helps to reduce the amount of buffering that is required whilst retaining the quality.
Lossy vs Lossless
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DuzD-LSanzM&list=PLCiOXwirraUA69WUAMYyFicC5qbQ4PGc4
Lossy Compression
Lossy compression is a compression technique that decreases file size by discarding bits of unnecessary data. This means that the original file cannot be recreated. Lossy compression will create a new image which is similar to the original, but has a reduced quality. Another example of lossy compression is used to reduce the file size of a sound file by reducing the bitrate used in the original.
All of the above use lossy methods of compression to save data and space. This isn't the best method to use as it gets rid of some of the data, so this would be a unsuitable method to use if the original file needs to be used. Lossy compression cannot be used on binary or text files because all data is needed to convey the correct meaning. People who would need the original file would be: Photographers, Audio Producers and Printing Firms. These could produce lossy compressed images for sample purposes or as draft prints.
Lossy compression is also ideal for online pages, as it allows faster load times due to a lower amount of data being loaded.
Lossy Methods
Some methods used are to delete sounds which are not heard, either because of the frequency or if another sound will drown it out. Images could be compressed more in the background than the foreground, the focus is the foreground so compression will not be noticed in the background. Also images could merge together adjacent colours just like the human eye. A pixel of black next to a pixel of white will actually be seen as two grey pixels.
Lossy compression formats:
- JPEG (image)
- MPEG-1 (video)
- MP3 (audio)
JPEG
JPEG stands for "Joint Photographic Experts Group". The JPEG format uses an algorithm in order to remove details that will not be seen by the human eye. It also reduces the quality of the background of the image since the main focus will be on the foreground or the main focus of the image. This helps reduce the file size whilst not reducing the main focus of the image.
MP3
MP3 stands for MPEG-2 audio layer 3. It uses different techniques such as removing inaudible frequencies and removing sounds that will be drowned out by louder noises. Bitrate is the number of bits a second that are encoded by MP3 per second. A higher bitrate will lead to a better quality sound at the cost of a larger file whilst a low bitrate will reduce the file size at the expense of sound quality. A variable bitrate is available in which the bitrate adapts to the sound in different parts of the recording.
Lossless Compression
Lossless compression is a compression technique that decreases file size while keeping all of the data. This means there is no loss in quality, and the original file can be recreated exactly as it was prior to compression.
This is possible because of repeating patterns in the data.
Examples of lossless compression methods include Run Length Encoding and Dictionary Based Methods. Run Length Encoding replaces repeating pixels or codes. Dictionary Based Methods rely on patterns within a file and are more effective with larger files. Each pattern can has an ID number.
Lossless compression formats:
- FLAC (Audio)
- WAV (Audio)
- PNG (Image)
- BMP (Image)
(Note that there are not many types of lossless video compression, the closest being H.264, as the file size tends to be smaller to start with)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M3zJT8gmfxE&list=PLCiOXwirraUA69WUAMYyFicC5qbQ4PGc4
Run Length Encoding
This method of lossless compression counts the bits that are repeated consecutively. For example, if a picture contained 3 red pixels one after the other, rather than storing each pixel individually, the file would instead store the pixel colour and the amount of times it is repeated.
However, if a file does not contain many repetitions then this method of compression can actually increase file size, as a single pixel would be stored as its colour and then the information that it is repeated only once.
Dictionary Based Methods
This is used when there are lots of repeating patterns of data.
For example, when writing a document about Computer Science, key words like "Computer Science" would be repeated throughout the document. Instead of storing the bit pattern for the word over and over, it stores the phrase in a dictionary with a reference number and stores the number in place of the phrase. ?This means that whenever the phrase is needed, it calls up the dictionary and replaces that number with the phrase.
A disadvantage of this method is that additional data is needed to store the dictionary as well as the file.
Difference between lossy and lossless compression
The main difference between lossy and lossless compression is the fact that when compressed, lossy loses some of the original quality*, whilst lossless retains all of the initial quality, hence the names "lossy" and "lossless".
Although sometimes lossy compression only removes the information that is not needed, for example it may remove some of the frequencies that cannot be heard by humans, so in this sense the reduced quality may not be detected.
The only other main difference is that, due to compression methods, lossy tends to be of a lesser file size when compressed, as some duplicate or unnecessary information tends to be left out, although this can also depend, as the original file might not have any duplicate or unnecessary information, in which case, the file size would be the same.
Revision Questions
try to add more questions on:
- lossless compression
- run length encoding
- dictionary based methods
- lossy vs lossless
Also '||' is the feedback for an answer, and could be greatly improved