Difference between revisions of "Flip Flops"
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Basic (SR) Flip Flops== | ==Basic (SR) Flip Flops== | ||
[[File:Bool-rs.gif|200px|SR-Flip Flop]] | [[File:Bool-rs.gif|200px|SR-Flip Flop]] | ||
| + | |||
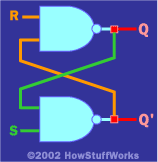
Basic flip flops are created using two NAND gates cross couples as seen in the image. | Basic flip flops are created using two NAND gates cross couples as seen in the image. | ||
==Problems with basic (SR) flip flops== | ==Problems with basic (SR) flip flops== | ||
| − | + | ==D and T type Flip Flops== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ==D and T type | ||
A flip flop has two inputs. One input is a control input. For a D flip flop, the control input is labelled D. For a T flip flop, the control input is labelled T. The other input is a clock input, labelled either with a triangle or CK. When a clock is drawn with a triangle like the ones below, these represent a positive-edge triggered clock, meaning that these can only change state when the clocks cycle is on a positive value i.e 1. When the clock is not on a positive value the bit stored within the flip flop is held i.e doesn't change. | A flip flop has two inputs. One input is a control input. For a D flip flop, the control input is labelled D. For a T flip flop, the control input is labelled T. The other input is a clock input, labelled either with a triangle or CK. When a clock is drawn with a triangle like the ones below, these represent a positive-edge triggered clock, meaning that these can only change state when the clocks cycle is on a positive value i.e 1. When the clock is not on a positive value the bit stored within the flip flop is held i.e doesn't change. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[File:D-FlipFlop.png|200px]] [[File:D-FlipFlopLogic.png|200px|Logic circuit for a D-Flip Flop]] | [[File:D-FlipFlop.png|200px]] [[File:D-FlipFlopLogic.png|200px|Logic circuit for a D-Flip Flop]] | ||
[[File:T-FlipFlop.png|200px]] [[File:T-FlipFlopLogic.png|200px|Logic circuit for a T-Flip Flop]] | [[File:T-FlipFlop.png|200px]] [[File:T-FlipFlopLogic.png|200px|Logic circuit for a T-Flip Flop]] | ||
| + | [[File:D-Type-ff.gif|200px|D type - Flip Flop]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Edge triggered D Type Flip Flop== | ||
Revision as of 09:49, 23 March 2017
Contents
What is a flip flop
A flip-flop is used to store binary data, and is a simple latching circuit.
Basic (SR) Flip Flops
Basic flip flops are created using two NAND gates cross couples as seen in the image.
Problems with basic (SR) flip flops
D and T type Flip Flops
A flip flop has two inputs. One input is a control input. For a D flip flop, the control input is labelled D. For a T flip flop, the control input is labelled T. The other input is a clock input, labelled either with a triangle or CK. When a clock is drawn with a triangle like the ones below, these represent a positive-edge triggered clock, meaning that these can only change state when the clocks cycle is on a positive value i.e 1. When the clock is not on a positive value the bit stored within the flip flop is held i.e doesn't change.

 200px Logic circuit for a T-Flip Flop
200px Logic circuit for a T-Flip Flop