Difference between revisions of "Network Topology"
(→Question 7) |
(→Question 7) |
||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
===Question 7=== | ===Question 7=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| + | |||
{ What is a bus topology? | { What is a bus topology? | ||
| type="()" } | | type="()" } | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | - Uses may cables to transmit data | ||
|| This is incorrect, a bus topology uses a single main cable as a backbone | || This is incorrect, a bus topology uses a single main cable as a backbone | ||
| − | + | + Uses one main cable as a backbone to transmit data | |
|| This is correct | || This is correct | ||
| − | + | - Connected devices in a network where each workstation has a dedicated cable to a central computer or switch | |
|| This is a star topology. A bus network uses one main cable as a backbone to transmit data | || This is a star topology. A bus network uses one main cable as a backbone to transmit data | ||
| − | + | - A wire with a bus in it | |
|| This is very wrong, a bus topology uses a single main cable as a backbone to transmit data | || This is very wrong, a bus topology uses a single main cable as a backbone to transmit data | ||
Revision as of 16:30, 14 November 2019
Overview
CraigNDave
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Fzho2mQQEuU&list=PLCiOXwirraUDvVsza-xO2mMwW9QBIa_FG&index=0
Computer Science Tutor
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iiU06wkTAuY&list=PL04uZ7242_M6O_6ITD6ncf7EonVHyBeCm&index=28
TRC PowerPoint
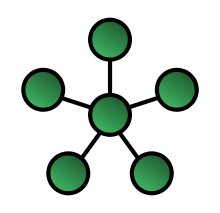
Star Topology
Nodes are connected to a host computer or hub that controls communication between devices. the hub or host computer regenerates any signal that it receives and passes it on. Only the intended recipient computer acts on the message.
All nodes have independent connections to the host. A cable failure on one branch of the network will continue to function normally and the failure will be easy to isolate.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| · Adding new devices is easy and doesn't disrupt the rest of the network. | · It requires a lot of cables. |
| · There are no data collisions. | · It is expensive to install. |
| · There is less traffic on the network. | · Needs professionals to maintain and up keep. |
| · A cable failure on one branch of the network will be easy to isolate. |
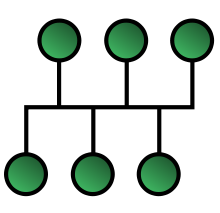
Bus Topology
When the bus (or line) topology is used each workstation is connected to a single cable (or backbone) which links all of the workstations.
The servers are connected to the main bus for data distribution to all the workstations.
Data can be transmitted in either directed along the main cable and workstations can communicate with other workstations.
A range of peripherals can also be connected to the main bus for shared usage. This could be a printer for example.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| ·Is cheaper to install as it used the least cable as the cost of network cabling (particular fibre optic), and the cost of the network cable installation can be significant | ·If there is heavy traffic the system performance will fall off dramatically |
| . | ·Data collisions due to shared cable |
| . | .Problems can be difficult to isolate |
Data Collisions - CSMA/CD
CSMA/CD stands for Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection. It is the protocol for carrier transmission access in ethernet networks. If two devices try to send a frame at the same time, a collision occurs and the frames are discarded. Each devices then waits a random amount of time and retries until the transmission is successfully sent.
Logical Bus Topology
A network could be wired using a star topology, but could act like a bus topology if all data traffic is sent to all machines.
Revision Questions
Question 1
Question 2
Question 3
Question 4
Question 5
Question 6
Question 7
Question 8
Question 9
Question 10
Question 11