Advanced Information Revision Notes
Contents
Recursion
Arrays
An Array is a data structure that allows you to store several values of the same data type.
They are static structures.
You must declare the size of the array when it is created.
Memory for entire structure is given when created.
Single Dimension
Each value can be accessed by the element number within the sequence.
Multi Dimension
You need to specify the dimensions when created (ie 3, 3 ).
It can still only store one data type, so it could be a 2 dimensional array of Integers
To access an element you need to give the number for each dimension.
Abstract Data Types & Dynamic vs Static
Queues
Stacks
Graphs
Graphs can be used to represent complex relationships, ie who knows who or how things are connected.
Vertex / Node
A point or location on the graph.
Edge / Arc
A connection from 1 node to another.
Weighted Graph
Edges will have a cost or value attached to it. This represents the cost or distance of using that edge.
Undirected
Edges are shown by a line. You can travel in both directions along the line.
If a node A is connected to node B, then node B is also connected to node A
Directed
Edges are shown with arrows, you can only travel in the direction of the arrow.
If a node A is connected to node B, then node B might not be connected to node A (it will be a separate arrow)
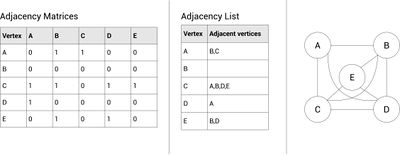
Adjacency Matrix
Used to store what is and isn't connected.
Essentially a table with the nodes across the top and down the sides.
You can enter a 1 or a weighting if the are connected.
0 if they aren't connected.
Adjacency List
Only stores what is connected.
For each node, simply list which nodes are connected.
Doesn't work for weighted graphs.
Matrix vs List
The advice is to use a matrix when you have a graph with many edges (Dense).
The advice is to use a List when you have few edges (Sparse)
Remember a list will also require additional processing to check the list of connections for a given node.
A matrix requires little processing, you can go direct to the location.
Trees
A tree is a specific type of graph.
- Must be connected
- Must be undirected
- Must have no cycles
Graph Traversal
Searching Algorithms
Sorting Algorithms
Optimisation Algorithms
Order of Complexity
Halting Problem
The halting problem asks:
‘Is it possible to write a program that can tell given any program and its inputs and without executing the program, whether it will halt?’
A method to do this for any program has been proven to not exist.