Client / Server Databases
Contents
Client / Server Issues
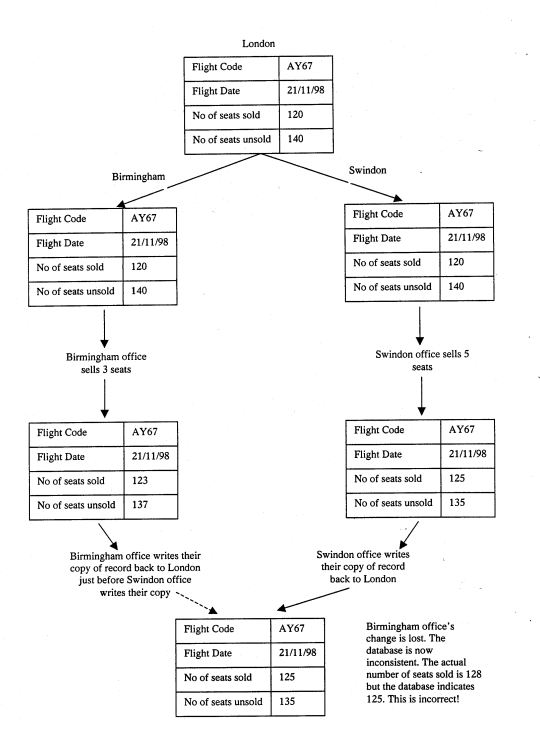
A client / server database allows multi user access, and the same record can be accessed at the same time by many different users and programs. This causes problems with Concurrent Access & Update. It is also called the lost updates problem.
Lost Update Problem
Resolving Issues
These issues can be solved by using features within the DBMS such as:
Record Locks
One solution is to lock the data to prevent any other changes from taking place while the database is been changed. This will be a temporary restriction on write access to the database, read access can still be given to users because that won't affect the ongoing change.
Once a user requests write access the database is locked, any other requests for write access will be refused. Other users can still read from the database
More complex locking mechanisms can be used, this could allow access to parts of the database not affected by the edits of another user. This could essentially lock a specific record or file, and could be used for example to d prevent bookings for a specific flight only yet still allow bookings for other flights. All locks are controlled by DBMS.
Serialisation
Serialisation is managed by DBMS and it ensures each transaction is carried out in the correct sequence. Without serialisation it could be chance / random which controls who has write access to the database. Those who request write access at the precise moment in time the database becomes unlocked, will get write access. If the correct sequence of requests is maintained then the DBMS can ensure all transactions are completed and in the correct order.
The DBMS will identify which transactions need serialising and provide a schedule for dealing with them.
Timestamp Ordering
Commands executed based on the timestamp for when the data was last written or read Each transaction will have a read and a write timestamp.
Commitment Ordering
In general all transactions are execute in order they are received, however each transactions will be assessed for the nature of it. The main factor considered will be the transactions impact on the database. A Transaction which will cause a deadlock will be blocked until any dependant action is complete.
An algorithm is used to create a commit order which avoids conflicts between transactions.