Encryption
This section needs expansion.
You can help by adding to it.
Definitions
Plain text - The data in human readable form.
Cipher - An encryption method or algorithm.
Key - The data used to encrypt or decrypt the plain text.
Cipher text - The encrypted data which can only be understood if decrypted.
Caesar Cipher
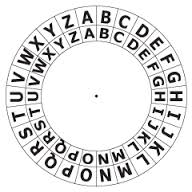
The creator was Julius Caesar. It is a substitution cipher which works by shifting letters by a number. The easiest way to look at a caesar cipher is to think of an inner and outer wheel, each wheel has the letters of the alphabet on its edge. When the letter A on both wheels are aligned the shift is 0 as in the image below:
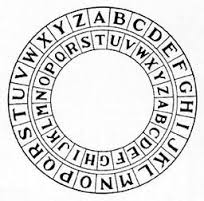
The shift turns the inner wheel a specific number of spaces. The image below shows a shift of 7:
Issues with Caesar Cipher
- There are only 25 possible keys, 26 makes the same output as the input so is just like a shift of 0. Any shift above 26, eg 45 will create an identical output as one of the shifts between 1 & 25.
- This cipher only encrypts letters so the letter spacing pattern will be identical to the plain text. You can therefore select an encrypted block of text and know it has a meaning. With brute force you could discover the exact shift (ie one shift will make a recognisable word).
- The key is constant throughout the text, so if you crack one word you crack the entire cipher text.
- With sufficient cipher text you could count the frequency of every letter used. The most frequent is likely to be the character for 'e', you can then calculate the shift.