Difference between revisions of "Sound"
(→Calculate Sampling Rate) |
(→Jack's Heading) |
||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
||Correct, you only need 16 bits to achieve CD quality audio. | ||Correct, you only need 16 bits to achieve CD quality audio. | ||
- 24 bit | - 24 bit | ||
| − | || | + | ||Incorrect, you only need 16 bits to achieve CD quality audio. |
- 32 bit | - 32 bit | ||
||Incorrect, you only need 16 bits to achieve CD quality audio. | ||Incorrect, you only need 16 bits to achieve CD quality audio. | ||
- 64 bit | - 64 bit | ||
||Incorrect, you only need 16 bits to achieve CD quality audio. | ||Incorrect, you only need 16 bits to achieve CD quality audio. | ||
| + | |||
| + | { According to Nyquist's Theorem, what should our sampling rate be? | ||
| + | | type="[]" } | ||
| + | - Half the original rate. | ||
| + | ||Incorrect, sampling at double the rate of the original audio will achieve the closest match. | ||
| + | - The same as the original rate. | ||
| + | ||Incorrect, sampling at double the rate of the original audio will achieve the closest match. | ||
| + | + Double the original rate. | ||
| + | ||Incorrect, sampling at double the rate of the original audio will achieve the closest match. | ||
| + | - Triple the original rate. | ||
| + | ||Incorrect, sampling at double the rate of the original audio will achieve the closest match. | ||
</quiz> | </quiz> | ||
Revision as of 16:30, 13 November 2017
Contents
[hide]Converting analogue to digital sound
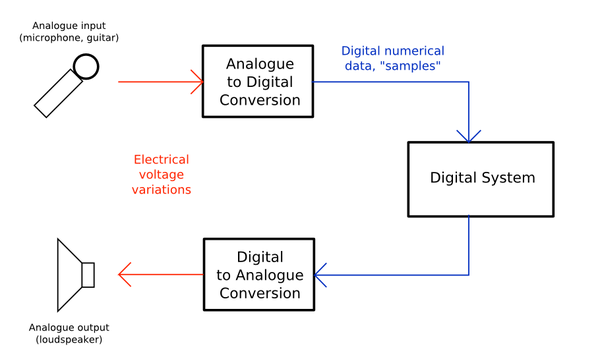
The following image demonstrates how sound files are created when they are inputted through devices such as a microphone:
Representing Sound
To store sound, a digitizer is needed to convert the analogue sound into digital sound. An analogue to digital converter carries out these conversions. 16 bit ADC is enough for CD quality sound. For High-Res audio, you can get audio files that are at 24 bit.
Sampling Rate
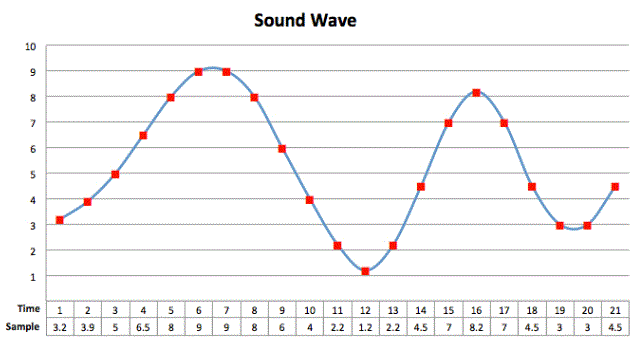
The sampling rate or frequency is the number of samples taken per second. It is measured in hertz (Hz)?. The higher the sampling rate the more accurate the representation of the sound. But the higher the sampling rate, the bigger the file size will be as there will be more data the is being stored
Sampling Resolution
The sampling resolution is the number of bits assigned to each sample. The number of bits assigned allows for a wider range of sounds to be displayed. For example, if only one bit is used it can only be either 1 or 0, giving an option of only two different sounds, where as if 8 bits are used there are a possible 255 different sounds that can be recorded and then replayed. In a way, your PC bleeper speaker is one bit as it only produces one tone when there is a error on your computer and then your actual speakers that you listen to music to will be 8 bit sound as you can play 255 different sounds on it.
Calculating File Size
A sound is sampled at 5Khz (5000Hz) and the sample resolution is 16 bits:
- There is 5000 samples per second & each sample is 2 byte (16 bits)
- 1 second of sound will be 5000 x 2 = 10,000 Bytes
- 10 seconds of sound will be 5000 x 20 = 100,000 Bytes
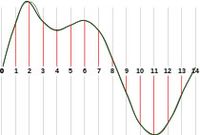
Sampling Process
Patrick's Heading
Pulse Amplitude Modulation(PAM) is the process which samples analogue signals and produces electrical pulses of height proportional to the signal's original amplitude.
Pulse Code Modulation(PCM) is the process of coding sampled analogue signals by recording the height of each sample in binary. PCM pulses can then be encoded in binary form.
Nyquist's Theorem
In 1928 Harry Nyquist found that in order to sample any sound at a similar quality to how it is in real life, you must use a sampling rate at double the frequency of the original sound. The result will be the closest possible to the original sound, because recording at double the frequency allows for all of the changes in the sound such as pitch to be captured digitally at a high quality.
Audio Compression
Audio compression is used to lower the space that a digital sound file takes up by removing sounds that humans won't be able to pick up listening to it. For example, in a song with guitar and drums, when there is a drum hit, the guitar will drown out in the background and become inaudible, so this data is removed to save memory, which is useful for devices like phones with a limited memory.
Audio Streaming
Audio streaming is a way in which audio/sound is broadcast to a user. It allows a user to listen to an audio file or watch a video without downloading the whole file, they only download a bit at a time... Which is the buffer.
Audio Streaming:
- Has a delayed start in order to allow it to buffer. - Plays sound from the buffer. - Has seamless play, unless connection is lost to the server/host. - Saves space on the hard drive. - Is harder to copy so reduces piracy.
Synthesising Sound
Sound can be synthesised with MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface), which records information about each note - such as duration, pitch, tempo, instrument and volume - and recreates that note when played. When using MIDI it is hard to replecate the proper soud as it would have to be played through note by note and would be a synthetic sound, in some cases it's good like in pop music but in other cases usually not. A MIDI link can hold up to 16 channels of information which can be routed to a seperate device for each channel.
Jack's Heading